With illustrative and scientific maps.. Learn about the reasons for the moderation of the atmosphere in the Levant in conjunction with the outbreak of heat waves on the European continent القارة
Arab weather - the southern and western parts of the European continent have gradually begun to be affected by the extension of a hot air mass of African origin that rushed from North Africa, and it is expected to spread to large parts of the European continent in the coming days, and on the other hand, it is expected that moderate weather and temperatures below normal rates will prevail in All over the Middle East, including the Levant.
A heat wave casts a shadow over Europe
It is expected that large parts of the west and center of the old continent will receive temperatures in the thirties, especially France, Spain and Portugal, this week, so that they are higher than their usual rates by more than 10 degrees Celsius, and this level is considered sufficient to launch the name of a heat wave by virtue of the climatic records of those countries.
Not only that, but it is expected that the eastern parts of the European continent will continue to be affected by cold air masses, in conjunction with the impact of the westernmost parts of the European continent and the Atlantic Ocean by another cold air mass, which means that the hot mass will continue to affect large parts of the west and center of the continent, but may extend to the British Isles. It may exceed it towards parts of Scandinavia, with hot weather and high humidity prevailing in those countries by the end of this week.
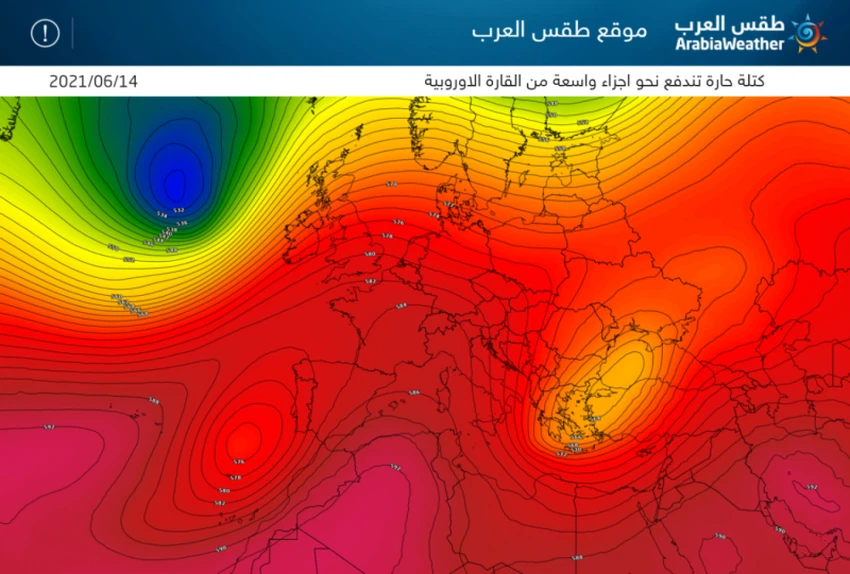
In complete contrast, the Levant lives in the reality of an atmosphere that is close to spring and temperatures below their normal levels, where mild to normal summer weather prevails and a humid and cold atmosphere in many areas during the night hours, and this atmosphere is expected to continue throughout the current week with the will of the God.
Climate situation for those interested
Many questions are asked about the absence of heat waves and their lack of impact on the Levant during the summer of this year and the prevalence of temperate weather, and the Arab weather answers that there are complex weather factors that constitute the final exit of weather conditions, and they are divided into two parts: surface and upper weather factors, i.e. in the upper layers of the atmosphere.
The stability of the distribution of air systems
When reviewing the prevailing weather factors, we note the rush of hot air masses towards large parts of the European continent and accompanying the control of a stubborn air rise in all layers of the atmosphere in the northwest of the African continent, which extends at intervals to the depth of the European continent, causing a significant rise in temperatures there, which worked to rush blocks Cold air towards eastern Europe, i.e. diverting the area of the air altitude, and there is also an air rise in the last aspects of Iran, extending to the countries of West Asia, which worked to confine the cold air mass east of the European continent with its extension towards the eastern basin of the Mediterranean, where this air system is almost the most prominent since the beginning of current month.
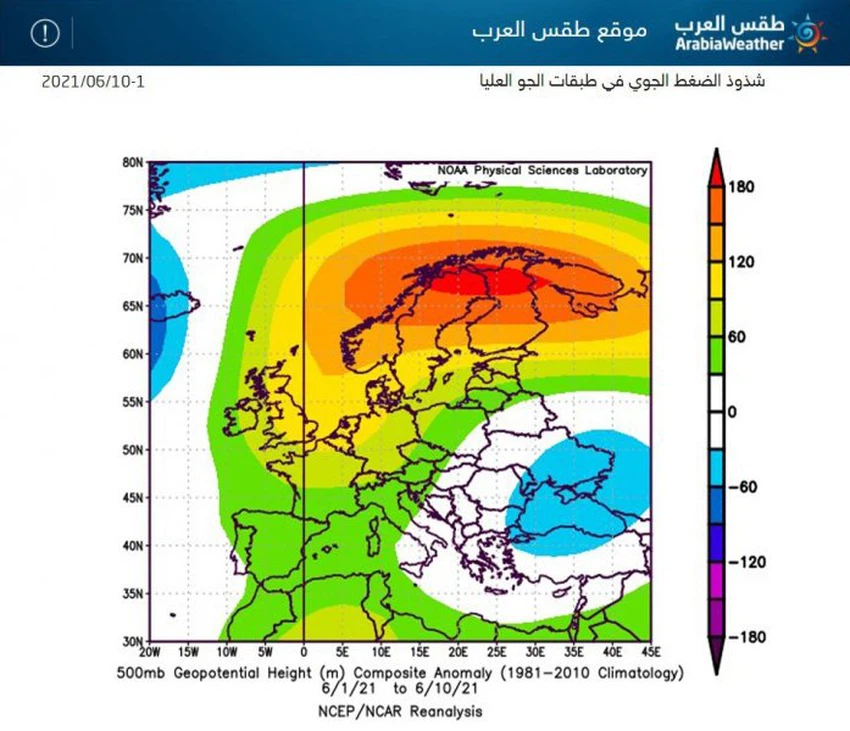
The Levant is positively affected by this air distribution, as it ensures the behavior of moderate air masses towards the eastern Mediterranean, as a result of a clear activity of the jet stream over the Arabian Peninsula and a strong building of the upper air altitude to the east away from the Levant. By reducing the heat through the infiltration of heat rays emanating from the surface of the Earth to the top, and this led to a softening of the atmosphere, and on the other hand, the surface was free of deep low atmospheric pressure centers, which contribute to the circulation of winds and bring hot masses, especially from southern Iraq and the Arabian Gulf Basin.
The role of water bodies
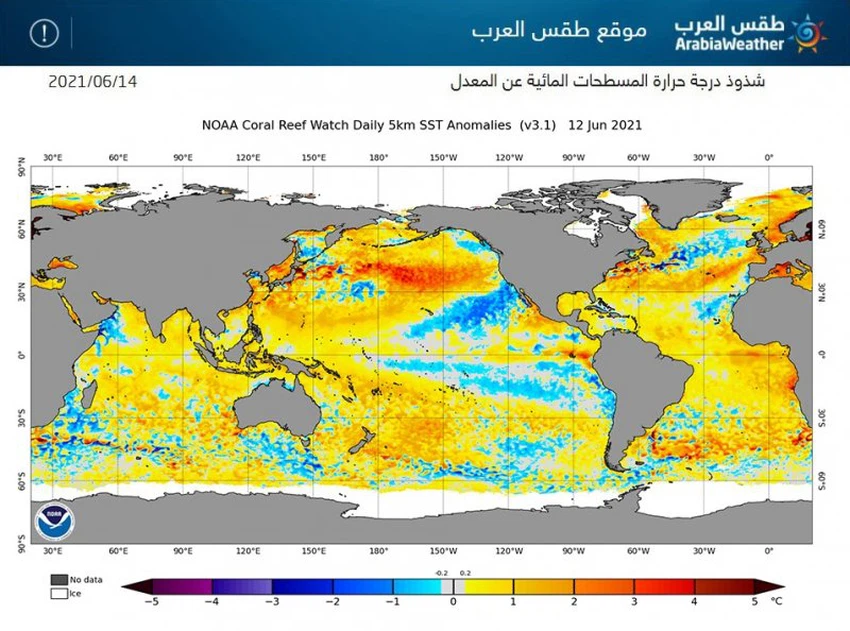
The distribution of air systems in this way comes as a result of sensing the cooling that occurred in many areas of the North Atlantic Ocean, which in turn worked to close the classic path of cold air masses, so that the depressions remained constant, ranging in place, especially in the west of the British Isles and Iceland, all the way to the island of Greenland.
What is the effect of global warming?
The term global warming has been widely circulated recently, linking heat waves and forest fires to it, and the Arab Weather explains that what is happening follows the so-called climate cycle, where ancient and documented historical records in international agencies show that the Earth’s climate over hundreds of years is affected by several natural cycles represented in Rising temperatures and increasing solar radiation in regions without the other, and there is no direct relationship as it is rumored that the rise in global temperatures pushes heat waves towards the region, as the atmosphere is pushing hot air masses towards certain regions without the other.
Browse on the official website