How do mountains arise? How does it get so big?
Weather of Arabia - Have you ever spent time contemplating the world around you and enjoying its natural beauty?! From vast oceans and dense forests to sweeping plains and steep hills, nature paints amazing pictures that capture the soul, all with the appreciation of God Almighty, who made everything a reason and allowed man to search and contemplate and realize with his mind the signs of God in his creation.
It may be one of the most beautiful natural features on earth, majestic mountain ranges, from the Himalayas to the Rocky Mountains, but how did the mountains get there? Did it fall from the sky as it is or was it formed in a certain way on the ground? This is what we will learn in this article, the types of mountains and how they originated.
How are mountains formed?
There are several ways in which mountains can be formed, and all of them take millions of years, and scientists believe that mountains were created by enormous earth forces that took a long time. The name of the theory of plate movement, and according to this theory, the earth’s crust consists of seven large, solid plates, and a number of smaller plates, and these plates are in continuous and slow movement, and these moving plates carry over them both the continents and ocean basins, and the movements that make up the mountains usually occur along The boundary between these plates.
Types of mountains according to the way they are formed
There are five basic types of mountains classified according to the terrestrial processes that led to their formation:
- Volcanic Mountains
- Fold Mountains
- Fault-Block Mountains
- Dome Mountains
- Erosion Mountains
Major mountain ranges may contain one or more of these types. For example, the Dividing mountain range in eastern Australia began as torsional mountains, and soon underwent erosion, then the eroding masses were raised higher to form refractive mass mountains.
volcanic mountains
Volcanic Mountains formed from the eruption of molten rock from the ground, accumulating above the surface of the earth; As a result, volcanic mountains consist mainly of igneous rocks, such as basalt and rhyolite, which form when they cool, and the molten material freezes.
- Such as Italy's Mount Etna, Vesuvius, and Japan's Mount Fuji.

torsional or folded mountains
Fold Mountains are formed when two tectonic plates meet face to face, at which point their edges can collapse, causing their edges to fold and wrinkle, somewhat similar to what happens to a metal can when crushed and wrinkled. From the rocks up.
- Like the Appalachian Mountains in the eastern United States, and the Alps in Europe
For example, the tectonic plates under India and Asia collided with each other more than 25 million years ago, and as a result formed the Himalayas, including Mount Everest, and the two plates are still pushing against each other, this means that the Himalayas are still growing even Today.
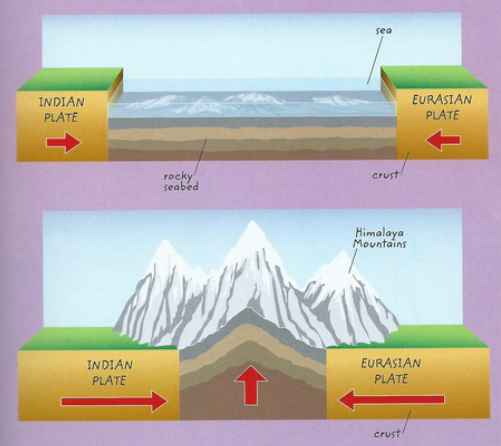
Torsional mountains often contain sedimentary rocks such as limestone, the material formed when sediments (crumbs of older rocks and the remains of ancient plants and animals) settled over the bottoms of water bodies, and then solidified. If these sedimentary rocks are exposed to extreme heat and pressure, some of them turn into metamorphic rocks such as marble and slate.
refracting or faulting massifs
Fault-Block Mountains are formed by cracks in the Earth's crust. A fault is a line in which rocks can move over each other. This process occurs when the rocks on one side of the fault rise relative to the other, and the rising blocks become mountains, while Overhanging blocks are known as depressions.

In fracturing mass mountains, the steep slope of the raised blocks along the fault results from rapid erosion of the exposed rocks on the other side of the fault, and by this erosion, the fractures and debris of these rocks are collected at the base of the mountain.

- Examples of this type of terrain can be found in the Upper Rhine Valley, the Vosges Mountains in France, the Teton Mountains in Wyoming, the Sierra Nevada Mountains in California, the Ronsuri Mountains in East and Central Africa, and the Harz Mountains and the Black Forest in Germany.
dome mountains
Dome Mountains were formed when geological forces lifted the Earth's crust into a bulge, or broad dome. High domes are more susceptible to increased erosion, as the sedimentary rocks that cover the dome are rapidly eroded, revealing what is beneath them of igneous and metamorphic rocks. Soon, these harsh lower rocks were subjected to erosion in irregular shapes, forming sharp peaks and valleys.
- Like the Black Hills of South Dakota, and Lake County in northwest England.

underfoot mountains
Mountain Erosion is formed after the erosion of a prominent rocky feature, such as the edge of a high plateau, where a newly formed mountainous area is exposed to the effects of wind, running water, ice and gravity. Distinctive landforms, including pyramidal peaks, knife-edge shapes, and bowl-shaped circles that can contain lakes.
- Like the Drakensberg mountain range in South Africa.

Browse on the official website