4 ways climate change contributes to extreme weather events
Weather of Arabia - This summer, the world witnessed more severe weather phenomena than usual, heat waves, deadly floods and massive forest fires. It seems that the impact of climate change has become more evident to the world, but how does climate change cause extreme weather events?
Emissions from burning fossil fuels (greenhouse gases) have trapped heat in the atmosphere since the beginning of the industrial age, and as a result, average global temperatures have risen by 1.2°C.
This extra energy is distributed unevenly across the Earth, and is pushing some weather phenomena to extremes like the one we saw this summer. Without a reduction in global emissions, such events will continue to recur.
Here are four ways climate change contributes to extreme weather events:
1. Hotter heat waves and longer effect duration
Although the shift in average global temperatures is slight, it has caused heat waves to become more frequent and extreme.
In the United Kingdom, warm periods have doubled in length in the past 50 years, and record heat waves in western Canada and the United States are getting longer and more intense.
In the western Canadian town of Lytton, temperatures reached 49.6 degrees Celsius, breaking the previous record by 5 degrees Celsius. Such an intense heat wave would have been virtually impossible without climate change .
Heat waves in western Canada and the United States were caused by a climate phenomenon called a "heat dome", where hot air in a region of high pressure is pushed down and locked in place, causing temperatures to rise over an entire continent.
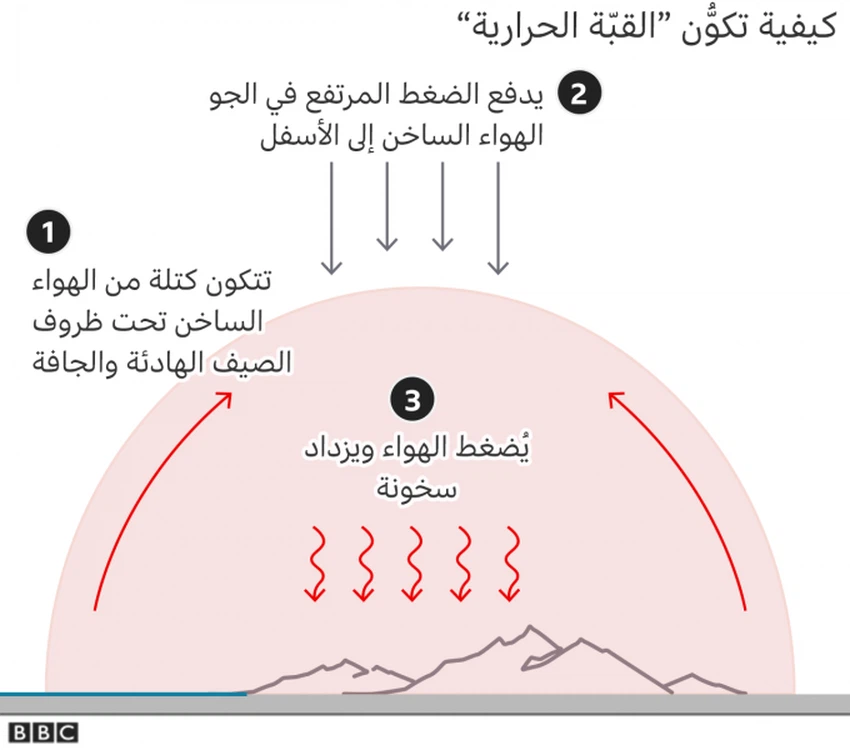
One theory is that higher Arctic temperatures (due to climate change) are slowing the jet stream, increasing the potential for thermal domes.
And weeks ago, a storm in the Pacific Ocean, fueled by warmer-than-normal sea temperatures, disrupted the jet stream. When a storm distorts the jet stream, which is made up of fast-flowing air currents, it's a bit like pulling a long jump rope at one end and seeing the ripples travel along it.
These waves cause everything to slow down dramatically and weather systems in the same areas can be disrupted for days in a row.

And the exceptional heat was not limited to North America this summer. In Russia, a heat wave caused temperatures to rise to a 120-year record. Northern Ireland broke records three times in the same week, while a new warming was recorded in Antarctica.
2. Exacerbation of heat waves and drought
As heat waves become more intense and prolonged, droughts can worsen. Less rain falls between heat waves, so the ground's moisture and water supply dry up more quickly.
This, in turn, means that the Earth is warming more quickly, which leads to a higher temperature of the air above the ground and a warmer atmosphere.
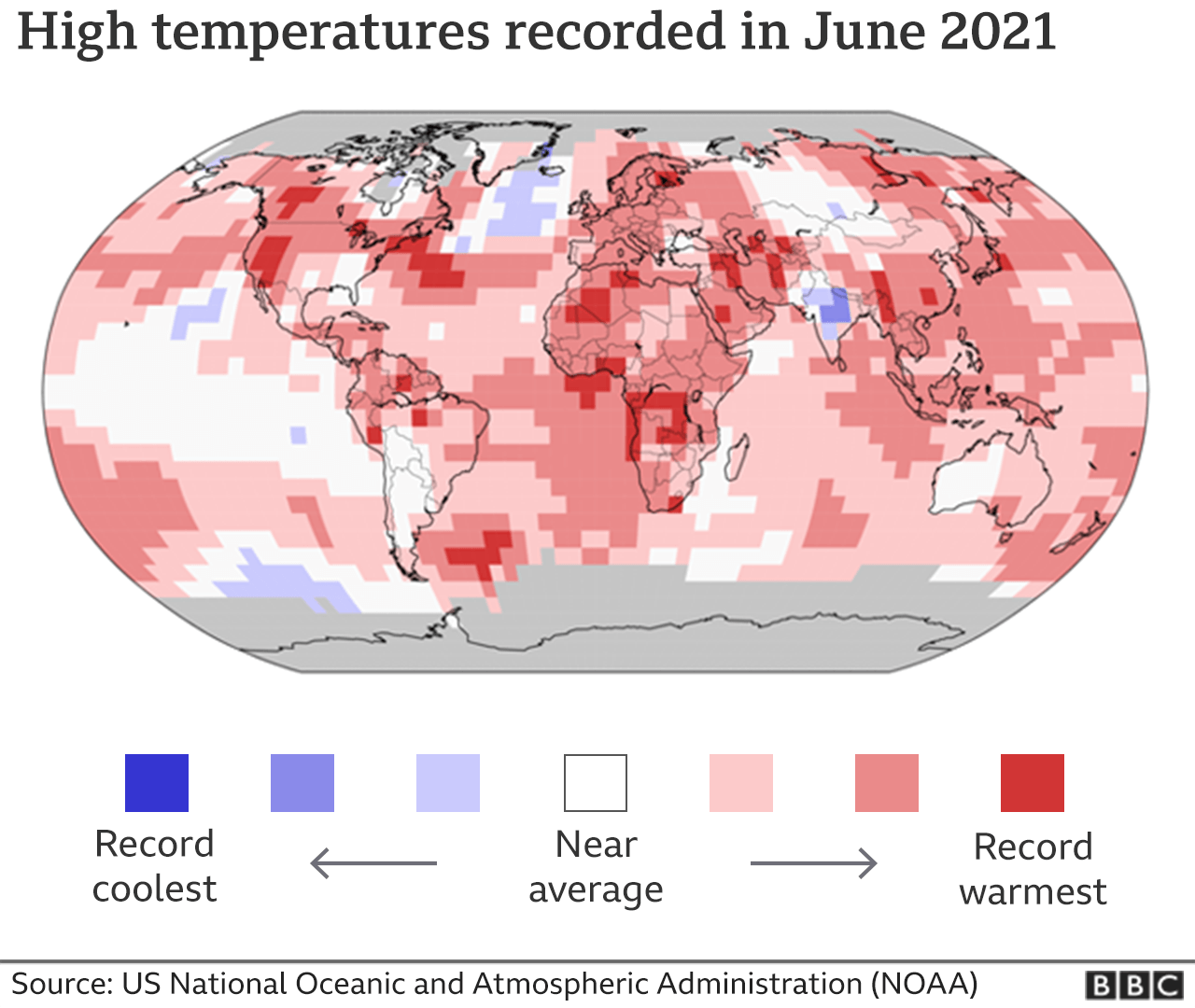
(In the figure is a map of the world showing the highest temperatures recorded during June 2021)
The demand for water for human and agricultural consumption also puts more pressure on the water supply, adding to water shortages and droughts.
By mid-July in the wake of early summer heat waves, more than a quarter of the US land was experiencing "extreme" and "exceptional" drought.
3. More forest fires
Forest fires can be caused by human intervention (such as manipulation or neglect), but natural factors play a large role in the occurrence of fires.
One such natural factor is the prolonged and intense periods of heat caused by climate change, which are drawing in more land moisture and vegetation. These dry conditions provide ideal fuels for fires, which can spread incredibly quickly.
The effect of the heat wave on the development of fires was seen in an explosive manner in western Canada this summer. Forest fires swept through several regions this summer, including forests in Siberia and southern Turkey, turning the forest floor into burnt trees and ash.
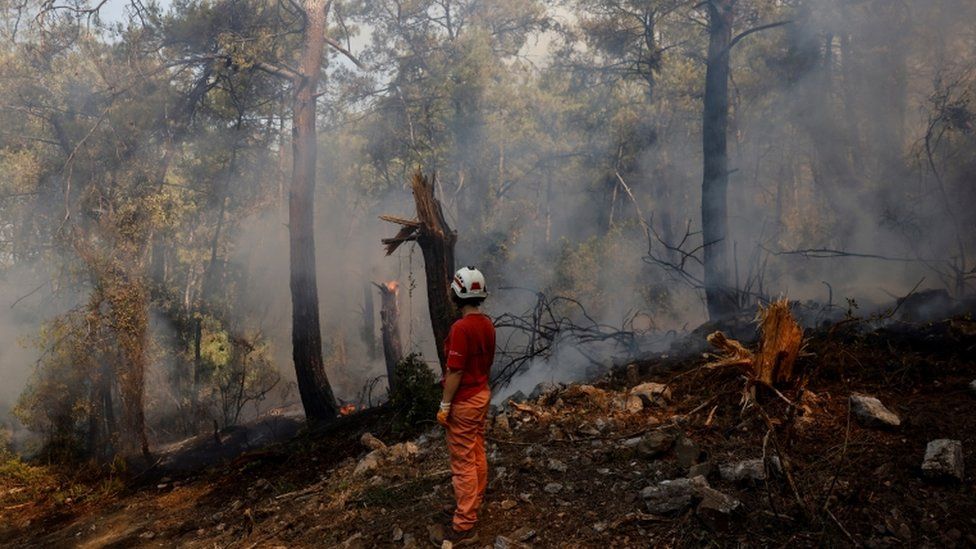

This summer, the fires developed very quickly, creating their own weather system, as pyrocomulonic clouds formed, these massive clouds produced lightning, and more fires were lit.
4. More heavy rain events
In a normal weather cycle, hot weather produces moisture and water vapor in the air, which turns into droplets to form rain. The higher the temperature, the more vapor there is in the atmosphere, which results in more heavy rain, and sometimes precipitation in shorter periods of time and over a smaller area.
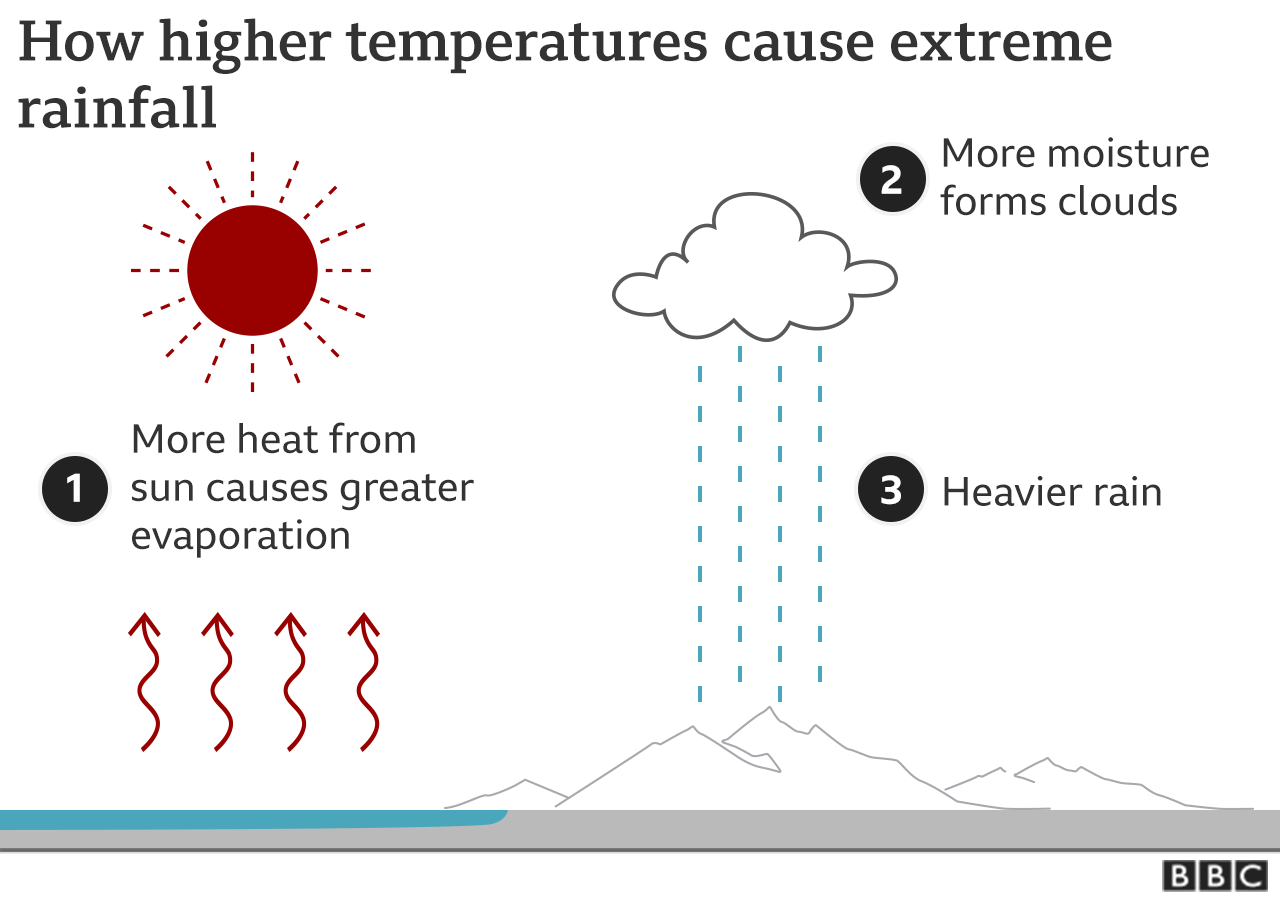
(The graphic shows how standard temperatures cause more rain. 1) More heat from the sun causes more evaporation 2) More moisture creates clouds 3) More rain
Historic floods in China, Germany, Belgium and the Netherlands have been witness to the devastating impact that heavy rainfall events can have, and these rainfall events are linked to the effects of climate change elsewhere. This water is elsewhere, and at a smaller scale, exacerbating floods as in the devastating floods of Germany and Belgium.
In conclusion, we are aware that weather around the world is always changing, but climate change is making that even more extreme. The challenge now is not only to reduce the human impact by increasing greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, but also to try to adapt and deal with extreme weather events, which we are already facing.
read more:
How can just 1.5 degrees Celsius of warming change life on the entire planet?!
Arabia Weather App
Download the app to receive weather notifications and more..



