How are weather forecasts and weather forecasts done
ArabiaWeather - The weather forecast process is a complex process that needs constant updates, and there are three important stages in which the weather forecasting process passes.
Stage (1): Monitor current weather conditions
At this stage, the details of the current weather are known, so in order to predict the weather in the future, we first need to know the current weather condition accurately, so that weather variables such as: temperature, precipitation, air pressure, winds, and humidity are measured over the course of 24 hours. An hour each day, it is passed to major weather forecast centers, which they use with satellite imagery to get a clear description of the current behavior of the atmosphere.
Stage (2): Calculate how the weather will change in the future
Meteorological centers and weather forecasting contain huge computers.These devices use data from meteorology to enter them into very complex equations that enable us to predict how weather conditions will travel, and the way the weather will change over time.
Stage (3): Using meteorological expertise to improve details
Meteorologists look at computer forecast models several times a day, and work around the clock to verify that weather conditions are going according to the way they were expected, and if not, the forecasts are modified before they are announced to people, especially if the modifications mean a change in Weather conditions, for example; If the temperature turns out to be lower than the expected temperature, this may make a difference to the formation of frost at night, and when it may be necessary to issue an alert to deal with frost.
Types of data that are measured in meteorology
(1) Data from space and satellites
Satellites give images of the entire globe from space, and meteorological satellites fall into two broad categories:
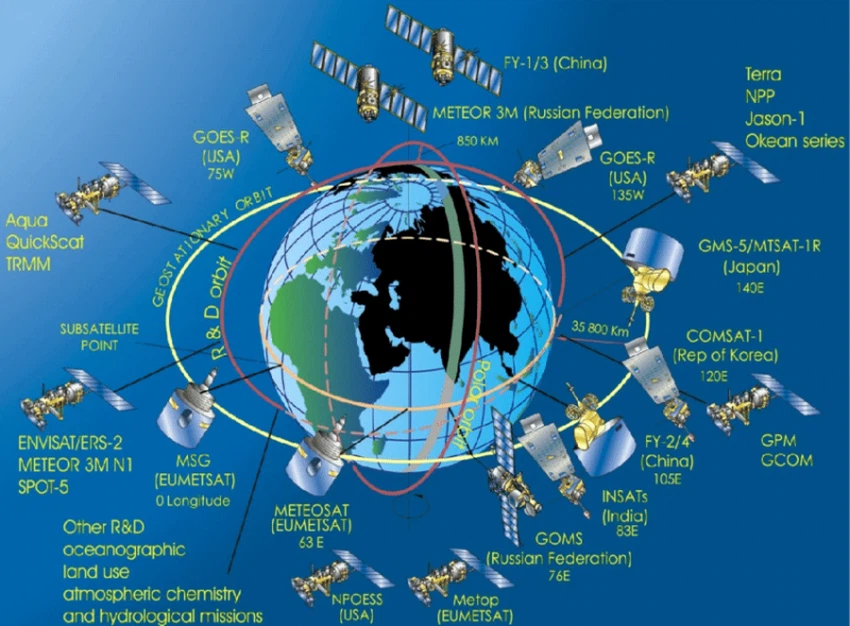
- Satellite with geostationary orbit (Geostationary Satellites):
These satellites are located above the equator at an altitude of 35,800 km, and they rotate once every 24 hours, at the same rate as the Earth, so they remain above the same place all the time to provide an unbroken series of images of the atmosphere in that place.
- Satellites orbiting around the pole (Polar Orbiting Satellites):
These satellites revolve around the pole at an altitude of 850 km, so that they are much closer to the Earth, which allows them to make more accurate measurements, and these satellites complete their orbit around the Earth every 100 minutes, during which they scan large areas of the atmosphere from the north pole of the earth to the pole Southern, where it passes over most of the Earth's tributaries at least twice during the day, and its orbits are synchronized with the sun, which means that it passes on the same part of the Earth at the same local time every day.
The images taken from both the geostationary satellites and the satellites that orbit the earth can be processed and analyzed to provide a lot of information about the atmosphere and the surface of the earth, and from this information that the satellites give:
- Images taken from geostationary satellites give a graphic impression of the movement of clouds, and infrared satellite images are used to measure the amount of clouds and their temperature, and to determine the rain-laden clouds, where the tops of the clouds are higher and cooler in white, while the surface of the earth and the lower clouds appear more A warm, dark color.
- Inferring wind speed and direction from the apparent movement of clouds between successive images.
- Accurately measure sea surface temperature from satellites.
- Measuring the amount of sea ice near the poles, and snow cover over land.
- Detection of fog, dust storms, pollution and volcanic ash.
- Probes placed on satellites measure the radiation emitted from the atmosphere and the Earth's surface, and these devices make accurate vertical measurements of temperature and water vapor, so that this information provides tremendous value for numerical models that predict the weather.
- Special radars on satellites orbiting the pole measure the back scattering over the oceans, which occurs due to small waves generated by the winds, and these small ripples on the sea surface with a wavelength of 5-20 cm, which are at right angles to the direction of the wind, and thus the velocity is derived from it Wind and its direction near the sea surface.
- Global navigation devices ( GPS ) on satellites are used in meteorology applications to identify areas of deep humid air that cause thunderstorms in hot summer days, by measuring the slowdown of the satellite signal arriving at a specific station, where the signal moves faster in dry air than in Air is loaded with water vapor.
- Altimetry devices on satellites give many data, especially over the oceans, such as the physical properties of the ocean, the height of sea ice, and tides, and phenomena such as El Niño and La Niña that occur in the Pacific Ocean can be tracked.
(2) Data from the surface of the earth
These data are provided as a measure of the weather that we are witnessing on the ground using a specialized observer and special tools, as most of the data is measured from the surface of the earth through monitoring stations distributed in different regions in each country, and among the important things that these stations measure are: Air temperature The temperature of the ground surface and soil, relative humidity, wind speed and direction, atmospheric pressure at ground level and its comparison with pressure at sea level, extent of visibility, amount and type of clouds and the height of their base, the amount of precipitation or snow accumulation, and after the data is recorded in the stations To process it, it is sent to a central collection system in the meteorological office, and in vital places such as airports, a trained observer is required to manually supervise the vital elements of the weather for the safety of the aircraft.
(3) Marine data:
Measurements are made both near the surface and in the depths of the oceans.
(4) Upper atmosphere data
The data of the upper atmosphere provides a three-dimensional structure of the Earth's atmosphere, it is important that there are measurements throughout the depth of the atmosphere that determine its three-dimensional structure. For this purpose, sophisticated monitoring systems are used to be able to measure the atmosphere in all its complexities.
(5) Radar image data
Weather radar provides accurate precipitation details at ranges of up to 1 km.
(6) Thunderstorm site
Thunderstorms and associated severe weather are localized.
Places covered by the weather forecast
Weather systems in one part of the world can have a rapid impact on other distant regions, so accurate forecasting requires monitoring operations not only in one country, but in many other parts of the world, so there is close cooperation in exchanging data between meteorological agencies in Different countries.
Long-term benefit of weather forecasting
Meteorological data also tell us how the weather today differs from the long-term average of the climate of a particular region, and how the climate changes over decades or centuries. In recent times there has been great interest in the risks that can result from climate change, so accurate meteorological data are considered Required as supporting evidence for decisions that governments can make in response to climate change.
Arabia Weather App
Download the app to receive weather notifications and more..



