Despite the cold weather..the earth is now at its closest point to the sun..what is the effect of that?
Weather of Arabia - Despite the cold weather and our winter season, the planet Earth passes today at its closest point to the sun, so what is the effect of that? Is this related to the weather and seasons?
The closest and farthest point of the earth from the sun
Because the Earth's orbit around the Sun is elliptical and the Sun is not in the center, the Earth passes at its closest point to the Sun in early January of each year, while the Earth passes in early July at its farthest point from the Sun.
Today (January 4, 2023) the Earth crosses at its closest point to the sun at 4:17 pm GMT. This closest distance between the Earth and the sun is called the “perihelion” or “perihelion”, a Greek word consisting of the two syllables “peri”. " which means near and "helios" meaning the sun.
And then the Earth will be closer to the Sun by about 3% (about 5 million km) than it is at the point of "apogee" (the farthest point from the Sun) in which the Earth passes in the month of July.

(An illustration of the sun and the Earth's orbit, and the difference in the distance between the Earth and the Sun during aphelion and perihelion. The Earth is slightly closer to the Sun at perihelion in January)
This means that the Earth is at its closest point to the Sun each year when it is winter in the Northern Hemisphere, and it is at its furthest point from the Sun in early July, during summer in the Northern Hemisphere.
So how does the earth's distance from the sun not affect the weather and the seasons of the year?
The Earth's orbit is not the reason for the different weather and seasons
Although the Earth's semi-circular orbit causes a difference in the Earth's distance from the sun, it is not the reason behind the existence of the winter and summer seasons on Earth, but rather the tilt of the Earth's axis during its rotation that causes the seasons to change.
When it is winter in the northern hemisphere (where most of the world's population lives), the northern part of the earth tilts away from the sun, while in summer, the northern part of the earth tilts towards the sun, so the temperature of that region of the earth rises because the solar radiation hits it The part of the land more directly.
The day when the Earth is most northward inclined to the sun is the summer solstice in June, and the day when it is furthest away from the sun is the winter solstice in December.
The Earth's orbit causes a slight difference in the number of days of the seasons
Summer is about 5 days longer than winter in the northern hemisphere
The direct effect of the Earth's presence at its closest point to the sun and its farthest is on the length of the seasons and not on the weather or temperatures, as the Earth moves faster in orbit when it approaches the sun in early January of each year, what does that mean?
The Earth is now spinning at about 30.3 km/sec, and moving about 1 km/sec faster than it was when the Earth was farthest from the Sun in early July. Thus, the Northern Hemisphere's winter (and Southern Hemisphere's summer) are the shortest seasons, as Earth moves from the December solstice to the March equinox.
In the Northern Hemisphere, summer lasts from the summer solstice in June to the winter equinox in September, about five days longer than winter. The opposite occurs in the Southern Hemisphere, where the Southern Hemisphere winter is approximately five days longer than the Southern Hemisphere winter.
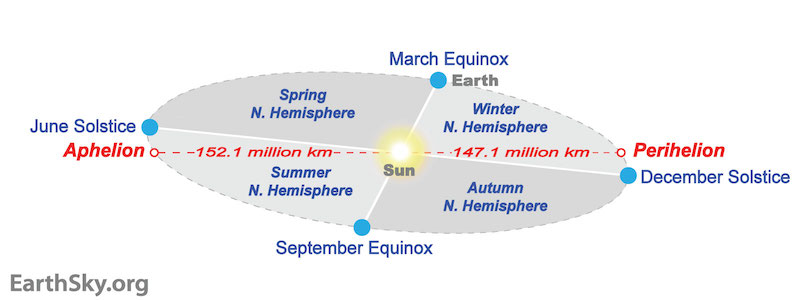
Illustration representing the elliptical orbit of the Earth, the positions of the equinoxes and solstice along the orbit, as well as the positions of the aphelion and perihelion, and the periods representing when the seasons occur during the Earth's orbit around the sun)
Also read: Despite the hot weather, the Earth passes at its farthest point from the sun
Arabia Weather App
Download the app to receive weather notifications and more..




