Weather System Analysis | Why do low pressure systems not reach the eastern Mediterranean basin despite the approach of mid-November?
Arab Weather - November is approaching its midpoint, and the eastern Mediterranean basin region has not been affected by any air depressions so far, despite the approaching start of winter from a meteorological perspective, which begins at the beginning of next December 2024.
Weather system analysis: Atmospheric dynamics do not allow low pressure systems to reach the eastern Mediterranean
Before delving into the main reason behind the absence of depressions in the eastern Mediterranean basin, we must explain in a simple way what atmospheric dynamics are.
Atmospheric dynamics: It means the movement of the atmosphere and its changes, and includes many different factors that affect the movement of winds, air currents, atmospheric pressure, temperature, humidity, clouds, rain, snow, thunderstorms, and other weather phenomena. Atmospheric dynamics includes a number of different factors such as the Coriolis force, temperature differences between different regions, the effect of the sun and moon, relative winds, and other factors.
Because the atmosphere is subject to a certain dynamic that depends mainly on a balanced movement between air masses, we see that areas of high-pressure activity are completely opposite to low-pressure areas as a natural balance for the atmosphere.
Cold air masses are rushing away from the area.
Returning to the scientific reason behind the cold air masses not reaching the eastern Mediterranean sufficiently to form depressions, and according to the map attached below of the movement of air masses in the 500 hectopascal layer, which is the layer in which air masses are active and depressions are formed, we notice the concentration of cold air masses rushing over western Europe, the Maghreb countries, northern Europe, Russia, northern America and Canada. Consequently, this dynamic forces the hotter air masses and highs to move towards the eastern Mediterranean basin region, and thus less humid and hotter than average weather and semi-stable weather affecting the region. Below is a map from the European Center showing the distribution of air masses in the 500 hectopascal layer:
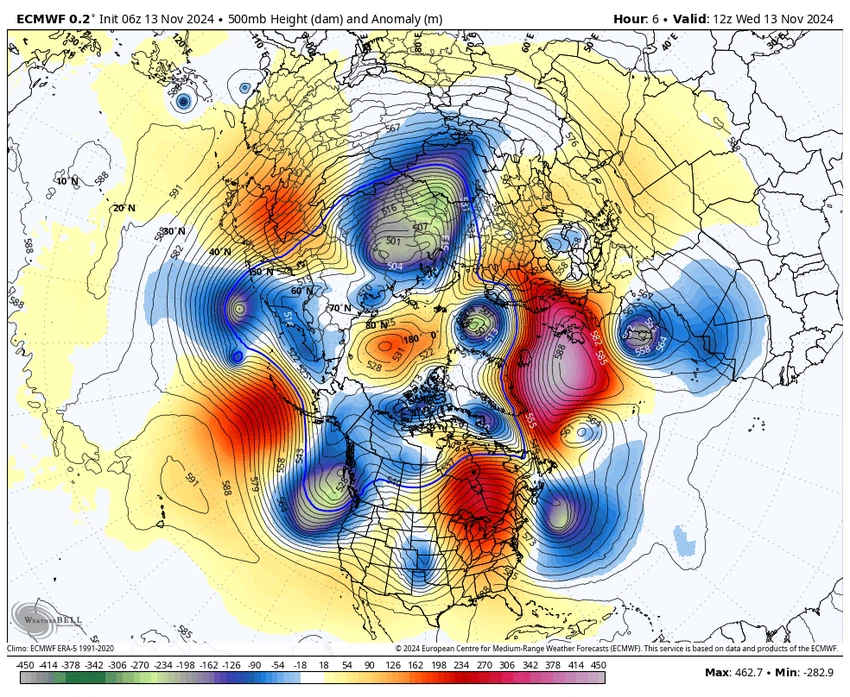
High pressure is centered near the area.
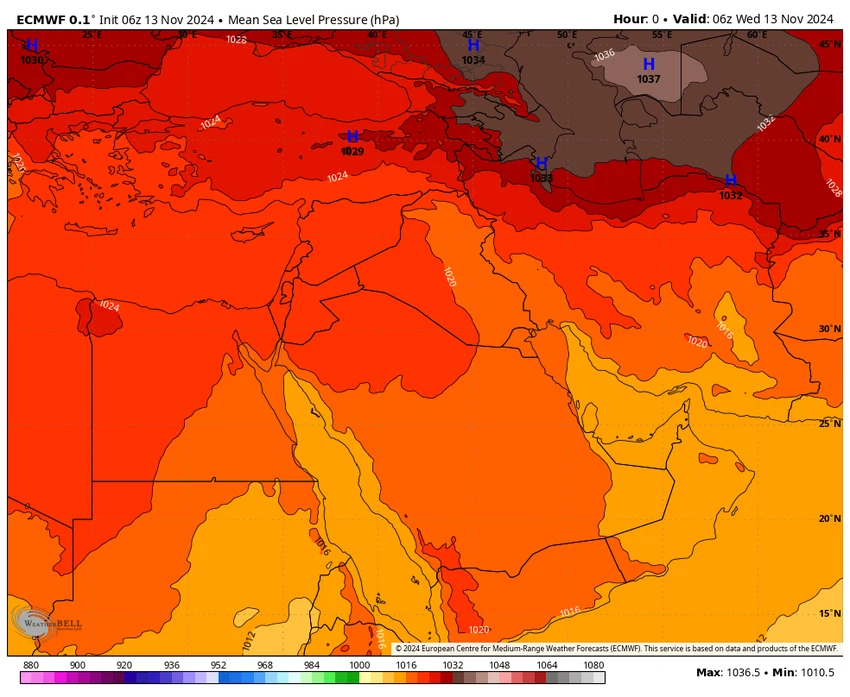
Experts at "Arab Weather" said that this process forces high air pressure to be concentrated near the region repeatedly due to the continued advance of the high pressure towards the region, as shown in a map from the European Center that shows the movement of surface pressures over the region during the current period:
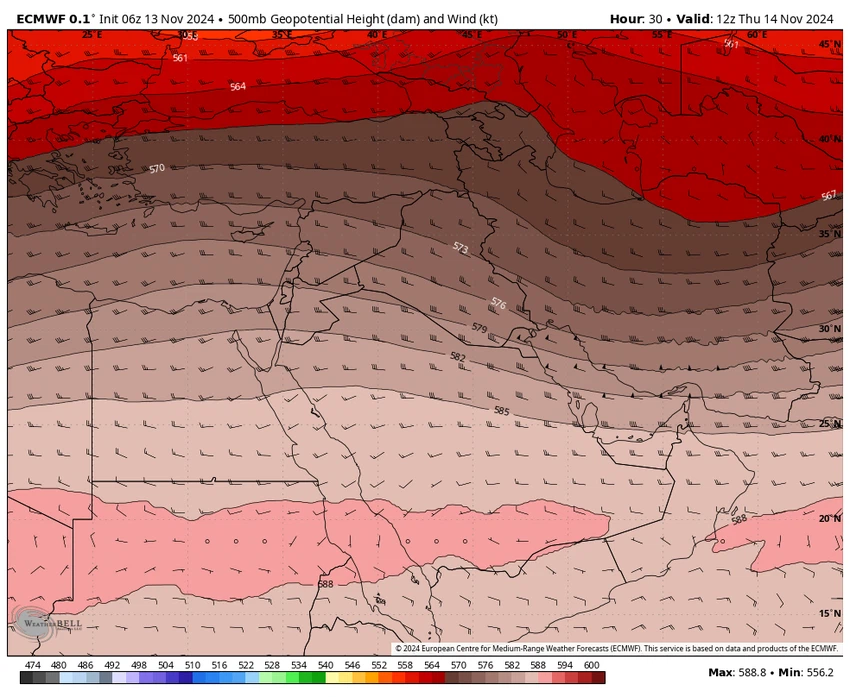
The map below shows a layer of 500 hectopascals above the region, which means that there is a high pressure and high air pressure affecting the region at the present time, preventing the arrival of cold air masses and thus generally stable weather:
The nature and movement of the polar jet stream
Looking up at the atmosphere, specifically the undulation of the polar jet stream, we find that the undulation of the polar jet stream does not serve the region primarily, as the cold air masses move according to the undulation of the polar jet stream, which directs the cold air masses away from the region during the current period, as shown in the map attached below:
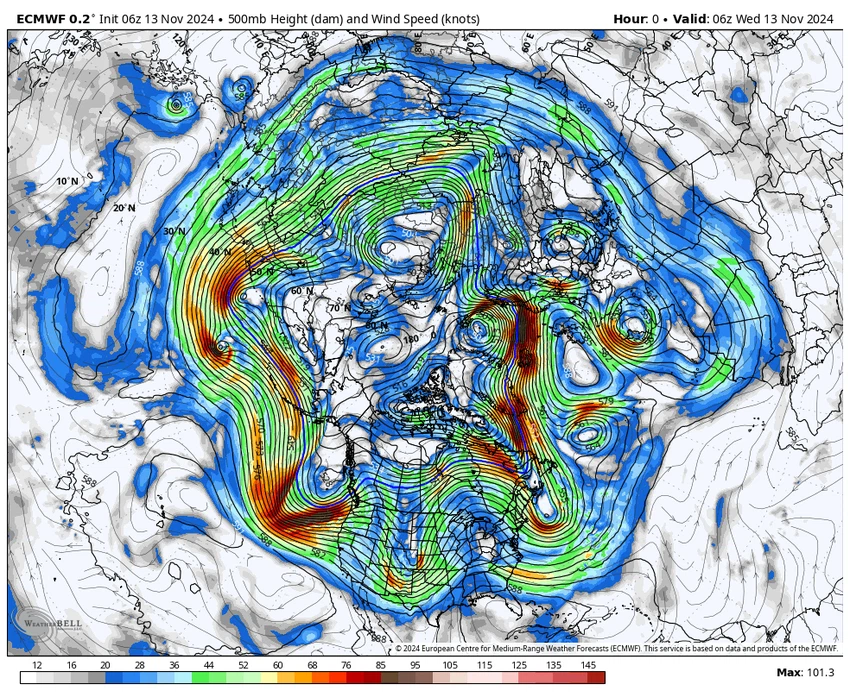
Arabia Weather App
Download the app to receive weather notifications and more..



