What is it cold and why does it sometimes rain in summer
ArabiaWeather - hail is defined as precipitation in the form of balls or ice pieces with a diameter between 5 mm - 15 cm, and hail differs from ice grains, where the diameter of ice grains (Sleet), which is sometimes called the small hail, is less than 5 Mm, and hail is often associated with thunderstorms because hail formation usually requires cumulonimbus or clouds that form as a result of convection and moist air currents rising strongly to the upper atmosphere.
How is hail formed?
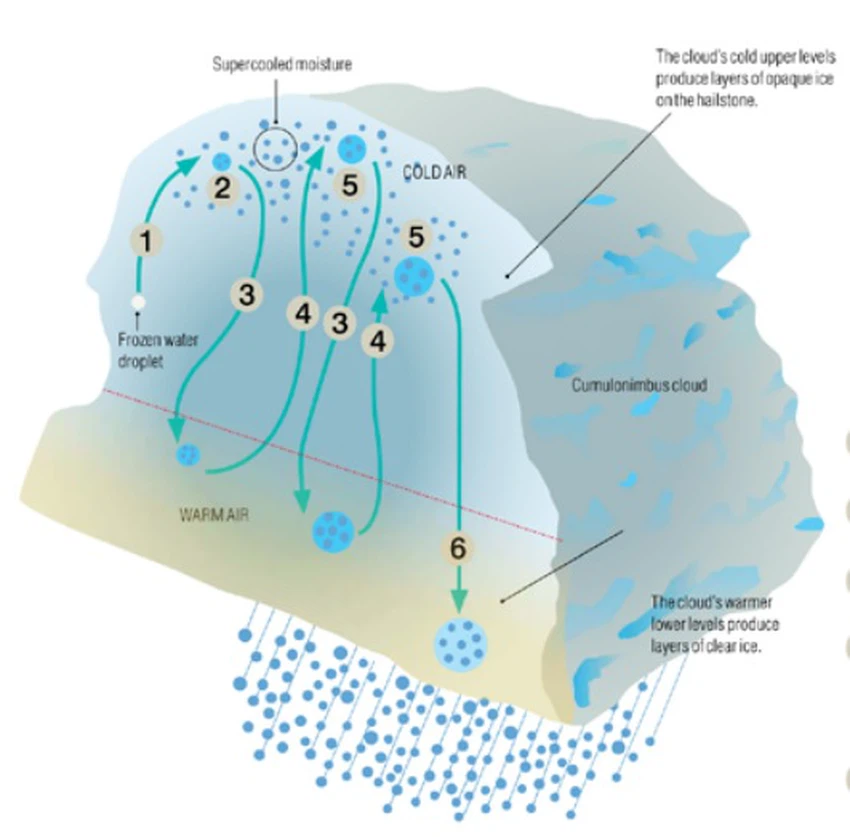
Hail grains are characterized by alternating layers of transparent and white (opaque) ice, which is formed due to irregular freezing rates, as water droplets freeze first slowly in regions where the temperature is slightly below zero degrees Celsius, allowing the trapped air to escape and produce clear ice (Transparent), but when the hailstones then move to a cooler area, freezing occurs rapidly, trapping the air and creating a layer of white ice.

The image shows a cross-section of the hail pill, showing layers much like the rings of a severed tree trunk, each layer representing the journey back to the area of super-cooled water droplets)
Hail storms and hail formation
When the air is heated, it rises due to its low density, and when the ascending air currents rise, the air temperature gradually decreases, and the air expands due to the decrease in pressure, which leads to condensation of water vapor and moisture in the air and clouds form, and during the condensation process water vapor releases latent heat, which leads to The air gives more energy to rise, so clouds grow larger and larger.
When the temperature decreases in the upper layers, the water droplets freeze, but they do not fall due to the rising air currents that push them up, so the frozen water droplets grow and increase in size, and during that their height changes between the warm air layer and the cold air layer, so the layers of ice accumulate at irregular rates of freezing between the freezing The rapid in the cold layer, and the slow assembly in the warmer layer, and in the end the hail pills fall when they reach the size that enables them to resist the rising air currents, and the hail from hail storms usually lasts about 15 minutes,
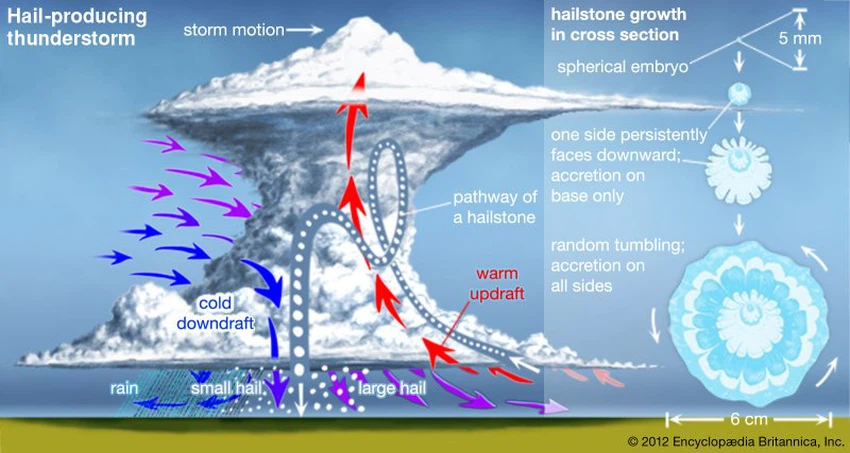
The growth of hail into large hail pods
The hail at first is very small and can be easily moved by the air currents. If the thunderstorm is not strong enough to prevent the hail from being suspended in the upstream, it will fall to the ground and it is usually small in size.
However, the small hail may get stuck in the upward stream if the upward current is strong enough, and then the hail pellets rise again to the area in which the supercooled water droplets are located, which did not freeze due to the lack of a core to freeze on. The cooling is at the top, so the hail is covered with a layer Others of ice and freeze, making them bigger and heavier, so they descend down, and the rising current pushes them up again, and so the more trips that the cold takes in the area where the drops of super-cold water are present, the size of it increases, until it reaches a stage where it finds it difficult to stay high. He falls to the ground quickly.
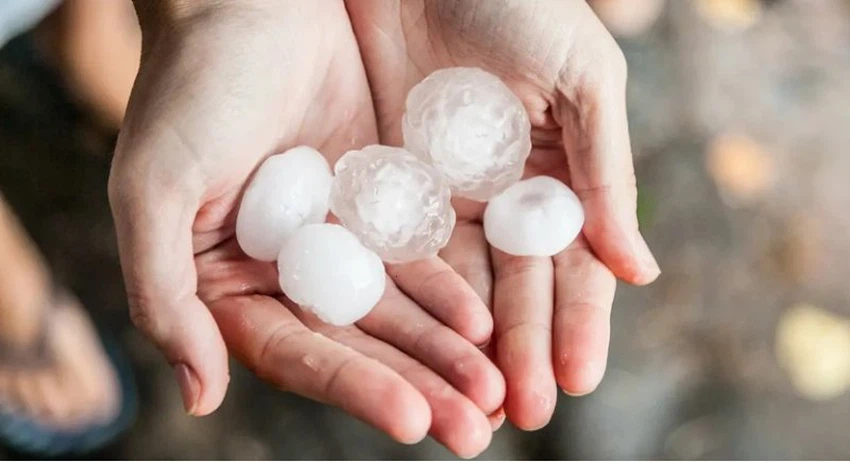
Vary the size and shape of the cold kernels
The size and texture of hail pellets may vary from one storm to another, and the size of hail is determined by the amount of time the hail pellets spend in the storm, and the shape of the hail depends on the layers in which it is formed, as opaque (cloudy) cold forms when very cold water freezes quickly, which is trapped Air bubbles in the ice, as for the cold with a clear appearance (transparent), it forms when very cold water freezes slowly, allowing the air to escape, and large hailstones can freeze and stick together, forming large, lumpy-looking hails.
The hail can grow to be the size of baseballs. The largest size ever officially recorded for hail pills fell outside Vivian, South Dakota on July 23, 2010, where it reached 20.32 cm in diameter, 45 cm in circumference, and weighed 0.88 kg, surpassing this previous record. Which was recorded for hailstorms that fell in Aurora, Nebraska, on June 22, 2003.
Why are large hailstones more popular in summer?
Despite the expectations that see hailstorms in the cold winter months, they are more common in spring, summer and autumn, especially in hot and humid areas, where appropriate weather conditions are available to form cumulus clouds that produce thunderstorms and hail, and hailstorms often form during the day Between mid to noon.
As for the size of the hailstorm, it is directly related to the strength of the thunderstorm. The greater the strength of the storm, the longer the hail period remains inside the cumulus cloud, and the greater its size, and hail particles with a diameter of more than 2.5 cm are considered "large", and therefore they are part of a severe thunderstorm, but most storms Not only containing one type of hailstorm, most thunderstorms feature at least six different hail sizes.

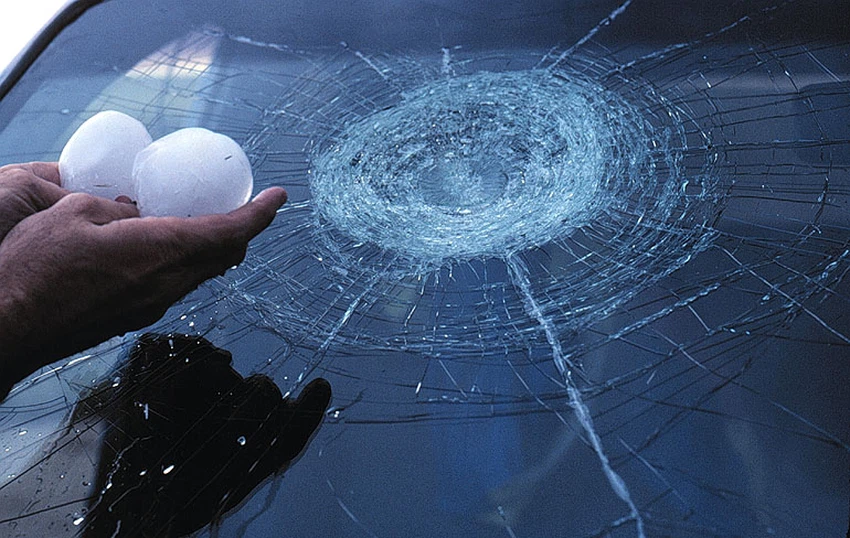
Hail damage
Cold may cause significant damage to buildings, vehicles, and agricultural crops, and it may also be dangerous to the animals exposed to it, especially if the hailstorms are large enough to cause the death of animals. One of the hailstorms that swept through the Denver metro area on May 8, 2017 caused $ 1.4 billion in damage. .

Arabia Weather App
Download the app to receive weather notifications and more..



