Why does snow take so long to melt despite the shining of the sun?
Weather of Arabia - After the snow falls and the earth is adorned with a white robe, the snow may stay for a long time before it melts and disappears, so why is the melting of snow sometimes delayed even after the sun shines and the temperatures exceed the freezing point?
Many physical characteristics are involved in the formation of snow in our atmosphere, how it accumulates on the ground, and how fast (or slow) it melts. Several variables control the speed of snow melting.
The most important factors that control the speed of snow melting
1. Snow Density:
Here we find two types of snow, dry ice, and wet snow that has a higher density, as wet snow contains more water than dry ice, and this reduces the number of hours that snow needs to melt after the temperature rises from the freezing point.
2. Air temperature:
Air temperature is one of the most obvious factors because the higher the temperature is above freezing, the faster the snow melts.
3. Solar radiation:
Shortwave radiation from the sun is what heats the earth and then the atmosphere, and the amount of solar radiation that an area receives depends on the cloud cover (the amount of clouds in the sky), in addition to the angle of the sun, so the greater the angle of the sun, the greater the efficiency of solar radiation in heating what comes into contact with him.
4. Wind speed:
The higher the wind speed, the more efficient the melting and evaporation processes that can accelerate the decrease in snow mass.
5. Long wave radiation:
Most of the earth's heat comes from the sun through shortwave radiation, but what many people don't know is that the earth itself emits thermal radiation because the core is also warm. Which acts as a barrier to longwave radiation, the snow can only melt from the top down, which increases the time it takes for the snow to melt.
6. The reflectivity of snow or Albedo :
"Albedo" is a term used to describe the total reflectivity of an object, and the reflectivity of newly fallen snow reaches 99%, which is the highest reflectivity of any natural material on Earth, and therefore snow reflects almost all of the sun's radiation, and this reflectivity is the reason for exposure to sunburn in winter when in Snow covered area, especially while snowboarding. As for old snow, its reflectivity reaches 60% - 70%, so it absorbs more solar radiation and thus can melt faster.
7 . latent heat:
Latent heat is the energy a substance needs to change from one state to another, such as a solid turning into a liquid or from a liquid into a gas. This is something a thermometer cannot measure. Snow does not turn into water once it reaches zero degrees Celsius. It takes some Time to build up enough energy for the solid ice to change into a liquid state, and because the latent heat of water is higher than that of air, it takes a huge amount of time and energy to melt ice compared to heating or cooling the air, which is also why when you take an ice cube out of the freezer, it doesn't instantly transform to a liquid in your hand.
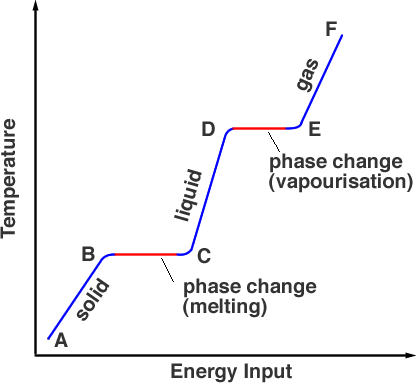
The graph shows that the temperature does not change in some periods despite the continuous addition of energy. These periods represent the phase change from ice to water and then from water to steam. Heating this snow to zero degrees Celsius does not consume much energy, but melting snow It requires a lot of energy and therefore a lot of time, which is why it takes so long for snow to melt when we pass the freezing point.
Also read: If water is transparent, why does snow appear white?
Arabia Weather App
Download the app to receive weather notifications and more..



